Simulations show this new technology can increase write speeds by up to 300 percent, reduce the number of write/erase cycles by 55 percent and cut power consumption by 60 percent.
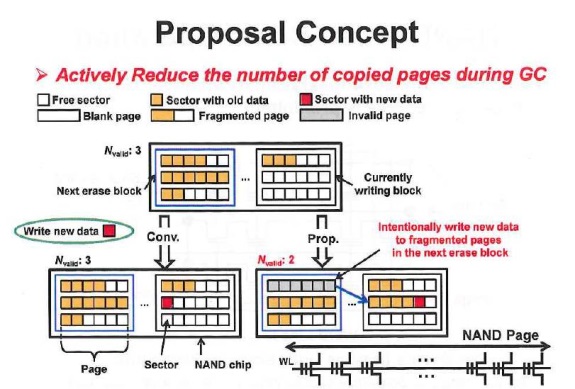
With NAND flash memory, it is not possible to overwrite data on the same memory area, making it necessary to write data on a different area and, then, invalidate the old area. As a result, data is fragmented, increasing invalid area and decreasing storage capacity. Therefore, NAND flash memories carry out "garbage collection," which rearranges fragmented data in a continuous way and erases blocks of invalid area. This process takes 100ms or longer, drastically decreasing the writing speed of SSD.
In September 2013, to address this issue, the research team developed a method to prevent data fragmentation by making improvements to middleware that controls a storage for database applications. It makes (1) the "SE (storage engine)" middleware, which assigns logical addresses when an application software accesses a storage device, and (2) the FTL (flash translation layer) middleware, which converts logical addresses into physical addresses on the side of the SSD controller, work in conjunction. This time, the team developed a more versatile method that can be used for a wider variety of applications.
The new method forms a middleware layer called "LBA (logical block address) scrambler" between the file system (OS) and FTL. The LBA scrambler works in conjunction with the FTL and converts the logical addresses of data being written to reduce the effect of fragmentation.
Full details at TechOn.