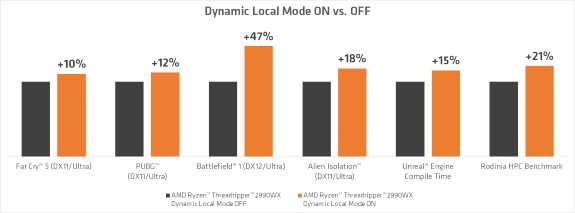
It's seems it's now Microsoft's job to integrate this into Windows, so users don't have to install tools to boost performance. According to AMD's own testing, this can boost Full HD gaming performance by 10 to 47 percent, when tested with the NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1080. Full details at AMD's blog.
What is Dynamic Local Mode?
Dynamic Local Mode is a new piece of software that automatically migrates the system’s most demanding application threads onto the Threadripper™ 2990WX and 2970WX CPU cores with local memory access. In other words: the apps that prefer local DRAM access will automatically receive it, and apps that scale to many cores will be free to do so.
What is the Benefit of Dynamic Local Mode?
In the applications we have tested to date, AMD has observed performance improvements of up to 47% with Dynamic Local Mode enabled. The below diagram shows a variety of games and applications aided by the new feature, and AMD expects other applications that we have not yet analyzed may also benefit. But we also want to be clear about the fact that not every application will see a benefit, as not every application demonstrates the threading behaviors that Dynamic Local Mode is designed to assist. Even so, it's clear that some processes really take a liking to Dynamic Local Mode and it's quite satisfying to see such a speedup from a new and free feature for your platform.
How is Dynamic Local Mode implemented?
Dynamic Local Mode is implemented as a Windows® 10 background service that measures how much CPU time each thread on the system is consuming. These threads are then ranked from most to least demanding, and the top threads are automatically pushed to the CPU cores that contain direct memory access. Once these cores are consumed by work, additional threads are scheduled and executed on the next available CPU core. This process is continuous while the service is running, ensuring the most demanding threads always get preferential time on cores with local memory. (As a corollary, insignificant threads are pushed to other dies.)