
Power envelope of Raptor Lake and Alder Lake
Raptor Lake-S is believed to be on track for a launch in the second half of 2022. This 13th Gen Core series promises better cache memory, LPDDR5X support, and up to eight high-performance cores in combination with up to sixteen high-efficiency cores.Raptor Lake-S will have a higher PL2 but lower PL4. According to Igor, Intel changed the definition of PL4 as this power stage has moved from Proactive to Reactive operation. PL4 is the absolute maximum power limit that can not be exceeded by the processor, it's a peak power limit that can not be reached for more than 10ms.
The PL2 value on the other hand may provide a better clue about the sustained performance draw of Raptor Lake-S when the CPU is under heavy load:
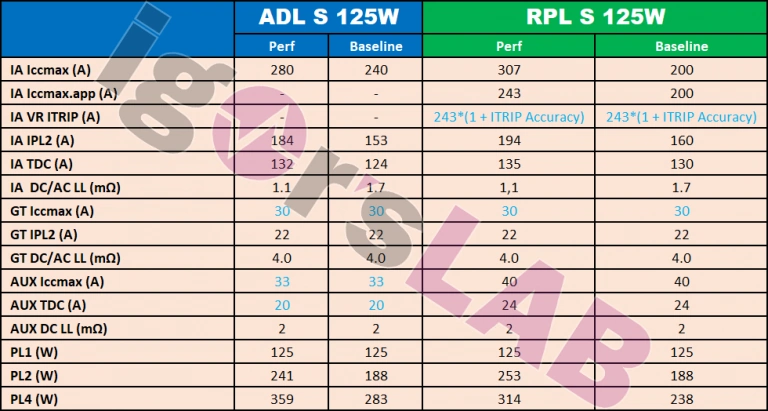
An easy-to-read comparison power data for both CPU series has been compiled by Igor. At the first glance, we learn that Iccmax current has increased for Raptor Lake, however, most users will be interested in PL1/PL2 and PL4 limits. While PL1 is the default power limit that aligns with SKU TDP, it’s the second power limit that might tell us more about next-gen CPU power and performance. Here we see higher PL2 values from 241 to 253W, but only for the Performance segment with Baseline unchanged at 188W. Interestingly, the peak power described by PL4 is lowered from 359W to 314W for the 13th Gen SKU.Below is the chart of the 125W TDP models, click through to VideoCardz for charts of the 35W and 65W TDP versions.
We'll have to wait and see how it plays out in the benchmarks, but it definitely looks like Intel is upping the power draw in an effort to close the performance gap with AMD's processors.