Posted on Tuesday, August 12 2014 @ 23:42 CEST by Thomas De Maesschalck
AMD announced details about Seattle, the company's upcoming eight-core ARM Cortex-A57 based server processor. Full details
at The Tech Report.
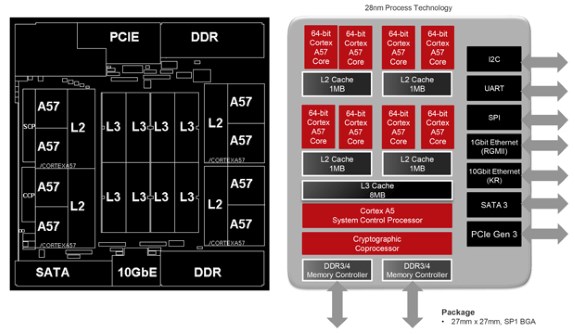
Seattle's eight 64-bit Cortex-A57 cores are arranged in four dual-core modules, each of which shares 1MB of L2 cache. That makes for 4MB of L2 cache in all. The four dual-core modules also have access to an 8MB pool of shared L3 cache, which links up all the cores, coprocessors, memory controller, and I/O. The L2 and L3 caches are 16-way associative with ECC protection, and Seattle's cache network (which also includes L1 instruction and data caches) is fully coherent, meaning there should be no discrepancies between instances of the same data stored at different levels of the cache.
Moving down to the memory controller, Seattle has dual memory channels that support either DDR3 or DDR4 RAM with ECC protection. Each of these 72-bit channels can accommodate a maximum of two modules (of the RDIMM, SO-DIMM, and UDIMM variety, depending on what hardware makers choose) with a peak transfer rate of 1866 MT/s. In all, each Seattle CPU can address up to 128GB of RAM spread across four 32GB modules.