Introduction
What is an alternator? An alternator is a part of a vehicle’s electric system that works alongside the car battery. It forms the backbone of the car’s charging system. Therefore, you should understand how alternators work and the role they play in your everyday commute.
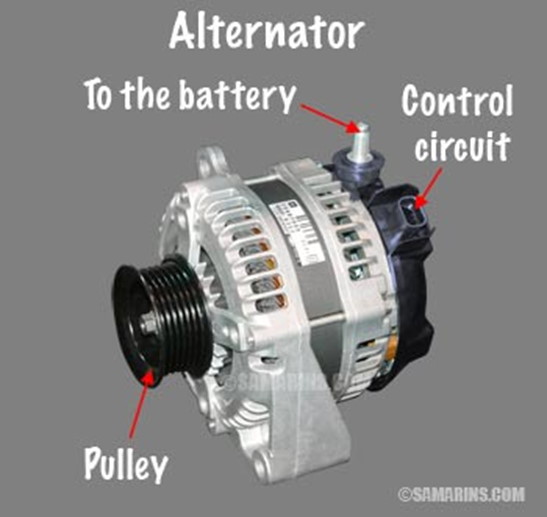
Your vehicle requires electric current to run, which means that it does not rely on the car battery alone. Although the battery under the hood is responsible for providing the energy required to start the vehicle, when the engine starts to run, the alternator takes control.
The Questions
Here is an ultimate guide that will answer your questions on how alternators work, including causes of failures and the solutions.
What are the components and functions of an Alternator?
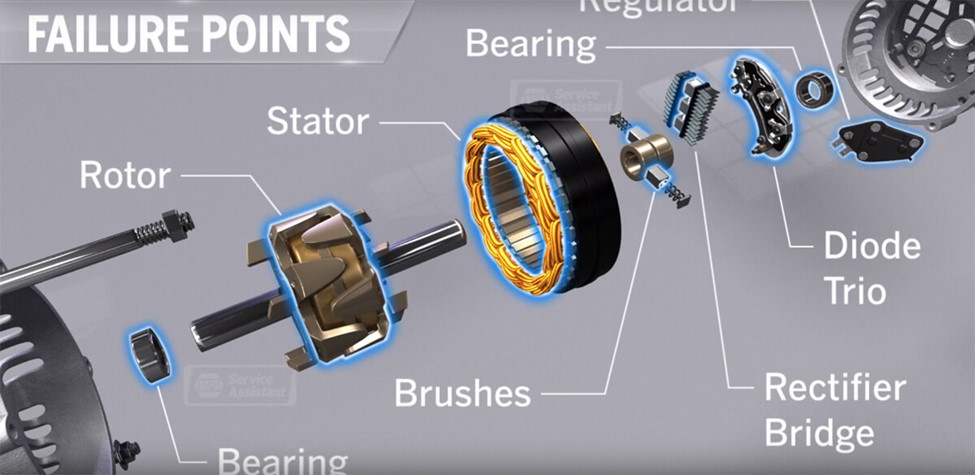
Alternators have many different components, and each of these components plays a certain role. These components include:
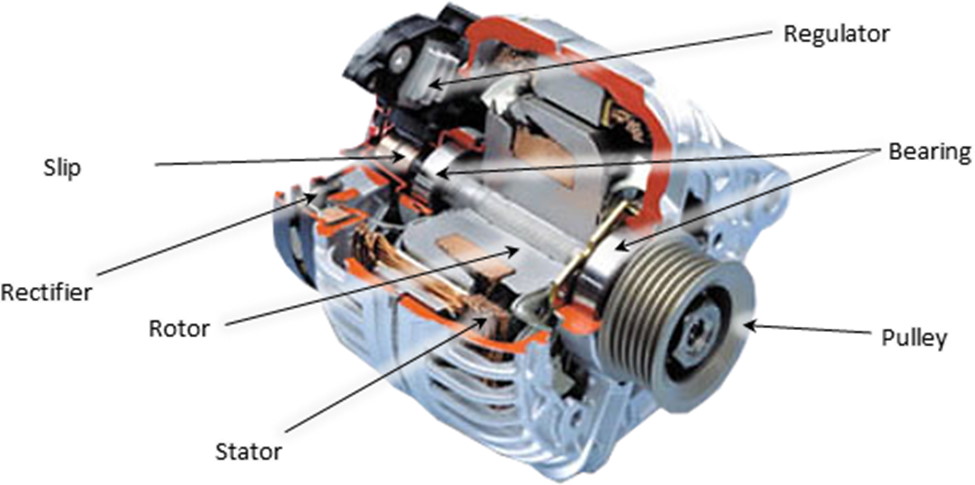
Regulator: The regulator controls the quantity of power dispensed from the alternator to the battery. The process charges the car battery and keeps it charged. However, regulators have different functions and how they work is dependent on their specifications.
Rectifier: In an alternator, a rectifier converts alternating current normally known as AC to DC, also known as direct current. The process happens during the charging process after the engine has started running.
Rotor: Rotor is the mass that is spinning inside the alternator. The spinning process is made possible by the drive belt and the pulley system in front of your car engine. The rotating electromagnet creates electromagnetism which produces an electric current.
Slip Ring: The main purpose of a slip ring is to provide power to the rotor and at the same time provide direct current to the car’s battery. Moflon slip ring is advisable.
Slip Ring End Bearing: As the shaft rotates, the bearings give support to the rotor shaft. It keeps the rotor shaft in place.
Stator: The stator is made up of many rolls of wire wound through an iron ring. It is placed outside of the motor and makes it possible to create an electric field which leads to the production of current.
Drive End Bearing: The drive and end bearing support the rotor shaft rotation.
Pulley: The main purpose of the pulley is to connect the drive belt system with the rotor shaft. As the drive belt system turns, it creates a rotation which turns the, and the charging process starts.
How Alternators Work?
A normal AD vehicle alternator has two parts:
Stator – It is stationary, and it appears out of the winding
Rotor – It rotates inside the inner winding
When a voltage goes through the regulator up to the rotor, it gives the rotor energy and makes it a magnet. The car’s engine drive belt rotates the rotor.
The rotation creates a magnetic field induced by the wound wires creating an AC in the stator winding. The AC is converted to DC using diodes to get the car battery charged. The regulator also controls the output voltage.
What are the Symptoms of a Bad Alternator?
Here are some signs that should indicate that you want to replace your car’s alternator:
Dim Lights: when your alternator is failing, some of the early signs that you will see is flickering or dim lights. It is an obvious sign at night, but you can also note the effects on the dome lights or dash lights. Moreover, if the lights become brighter as rotation per minute (RPM) picks up, then that is a sure sign that your alternator is failing.
Strange Noises: The pulley belt stretches as it ages, and in such a scenario, it cannot spin the alternator pulley with the efficiency that it should. In such a case, you will notice that it is producing squealing sounds. The problem can also balloon and lead to wear of the internal bearings which cause grinding or growling noise.
Electrical Problems: One of the main things that can indicate your alternator is failing us electrical car equipment shortfalls including windows and power seats being slow when operating them. In extreme cases, the devices will stop working altogether, including the car radio failing to function.
Engine Stalling: If your car engine suddenly stops when you are driving, there are high chances that the problem is with the alternator. A good amount of electrical power is required for fuel injection, and when the electric current is low, the engine will stall.
Dead Battery: The alternator keeps the battery charge high, so when it fails, the battery will lose its capacity and eventually it will be drained.
Does an Alternator require a battery to work?
How alternators work is more complicated than many people imagine. In response to the question above, the general answer is no, but there are some exceptions. Look at these different scenarios.
1st Scenario: An alternator does not require a battery to power a car. If the vehicle’s engine is already running and the battery fails, the alternator will continue running the car until the time you will switch off the engines.
2nd Scenario: If there is any chance that there was residue magnetism in the rotor capable of generating a voltage, the car will still run. However, if there is no residual magnetism or a source of voltage, the alternator will not work.
Can an Alternator Charge a Dead Battery?
Anyone who drives a car knows that jumper cables are lifesavers. However, you should know that anytime you are using jumper cables to start your car, you are placing a heavy load on your alternator and your battery.
An alternator cannot charge a dead battery because alternators do not have permanent magnets. They rely on the power from the battery to create a magnetic field which produces AC.
If you have an alternator attached to a dead battery and then start spinning the alternator, it cannot charge the battery because it cannot produce energy on its own. However, it is possible to give the stator some energy if the battery has some slight charge.
Conclusion
Many people wonder how alternators work, but the most important question is how the part they play in making our lives more convenient. Alternators are the main primary sources of all the electrical energy consumed across the planet.
They are the largest energy converters. Always remember that when you are driving your car or switching on a lamp switch, somewhere, an alternator is making that possible.


