Gas giant Jupiter is the solar system's largest world with about 320 times the mass of planet Earth. Famous for its Great Red Spot, Jupiter is also known for its regular, equatorial cloud bands, visible in very modest sized telescopes. The dark belts and light-colored zones of Jupiter's cloud bands are organized by planet girdling winds which reach speeds of up to 500 kilometers per hour. On toward the Jovian poles though, the cloud structures become more mottled and convoluted until, as in this Cassini spacecraft mosaic of Jupiter, the planet's polar region begins to look something like a brain!
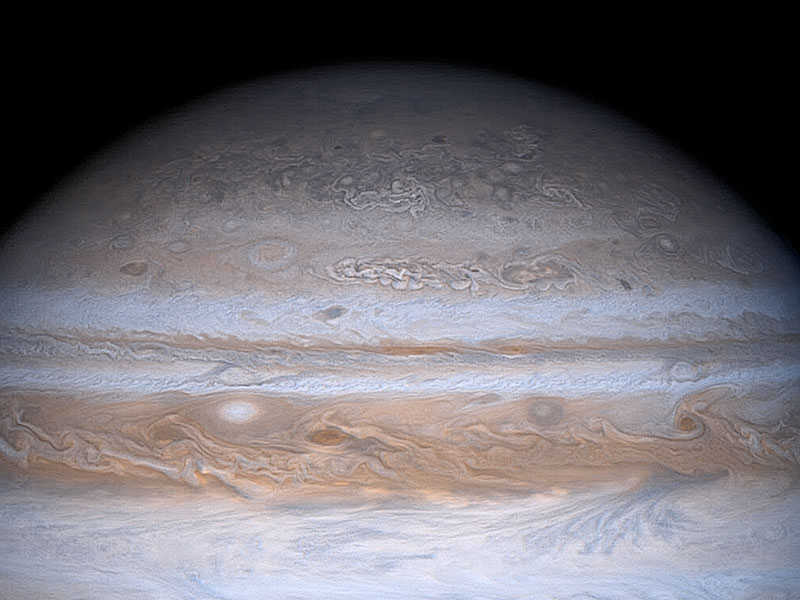
This striking equator-to-pole change in cloud patterns is not presently understood but may be due in part to the effect of Jupiter's rapid rotation or to convection vortices generated at high latitudes by the massive planet's internal heat loss. The Cassini spacecraft this dramatically detailed view of Jupiter in 2000 December during its turn of the millennium flyby enroute to Saturn.